Dependency Scanning [ULTIMATE]
Introduced in GitLab Ultimate 10.7.
Overview
If you are using GitLab CI/CD, you can analyze your dependencies for known
vulnerabilities using Dependency Scanning, either by
including the CI job in your existing .gitlab-ci.yml file or
by implicitly using Auto Dependency Scanning
that is provided by Auto DevOps.
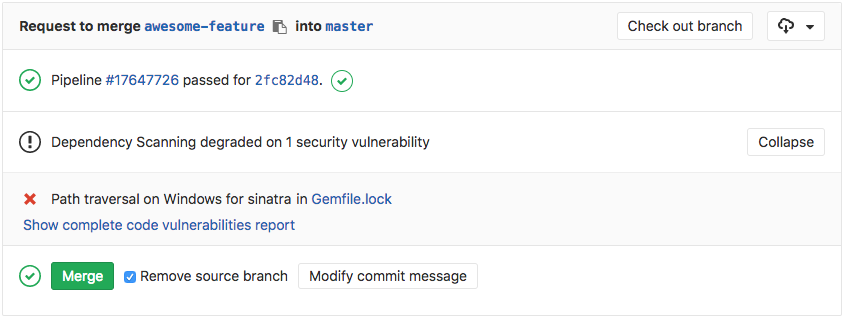
Going a step further, GitLab can show the vulnerability list right in the merge request widget area.
Use cases
It helps you automatically find security vulnerabilities in your dependencies while you are developing and testing your applications. E.g. your application is using an external (open source) library which is known to be vulnerable.
Supported languages and dependency managers
The following languages and dependency managers are supported.
| Language (package managers) | Scan tool |
|---|---|
| JavaScript (npm, yarn) | gemnasium, Retire.js |
| Python (pip) | gemnasium |
| Ruby (gem) | gemnasium, bundler-audit |
| Java (Maven) | gemnasium |
| PHP (Composer) | gemnasium |
Some scanners require to send a list of project dependencies to GitLab central servers to check for vulnerabilities. To learn more about this or to disable it please check GitLab Dependency Scanning documentation.
How it works
First of all, you need to define a job named dependency_scanning in your
.gitlab-ci.yml file. Check how the dependency_scanning job should look like.
In order for the report to show in the merge request, there are two prerequisites:
- the specified job must be named
dependency_scanning - the resulting report must be named
gl-dependency-scanning-report.jsonand uploaded as an artifact
The dependency_scanning job will perform an analysis on the application
dependencies, the resulting JSON file will be uploaded as an artifact, and
GitLab will then check this file and show the information inside the merge
request.